This document contains information on how to install, configure, and use the product.
Web Administration for Microsoft® Windows NT® Server
enables you to remotely administer Microsoft Windows NT Server using existing HTML browsers running
on Microsoft Windows®, Macintosh and UNIX platforms. Web Administration is not
designed to replace existing administrative tools for Windows NT Server; instead, it is to enable
you to perform limited administrative tasks when you are "roaming," away from your usual
workstation and without access to traditional tools. Web Administration is a tool that is implemented
to work in conjunction with Microsoft Internet Information Server 4.0 (or higher).
The Web Administration tool is intended for existing Windows NT Server
administrators who have performed tasks with the regular administrative tools on Windows
NT 4.0.
How the Software Works
You can install the Web Administration software on any server that runs
Windows NT Server 4.0 and Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS) v4.0 or higher.
Installing the Web Administration software on the server causes the server to publish web
pages that include forms you can use to administer that particular server.
You can then use any web browser that supports either Basic or Windows
NT Challenge Response authentication. You simply type in the address section of your
Browser "http://<your_server_name>/ntadmin/default.asp", and
begin administering the server.
Administrative Tasks You Can Perform
The tasks most commonly performed by roaming administrators are
supported by Web Administration. The table at the end of this section lists supported
tasks.
The actual interface is a series of HTML pages that the Administrator
navigates through using a web browser. The interface is intended for administrators
familiar with existing administrative tools (such as User Manager, Control Panel,
Performance Monitor, etc.). Tasks to be performed are extremely atomic, and the pages
include some Wizard-like explanations to assist the user.
Some of the Tasks You Can Perform with Web Administration for Microsoft Windows NT Server
| Account Management |
|
| Printer Management |
|
| Remote Access |
|
| Share Management |
|
| Session Management |
|
| Server Management |
|
Web Administration supports several modes of security. Each server you administer must
support Basic authentication, Windows NT Challenge Response security, or both. In
addition, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) can be used with either or both of these modes of
security for encryption of your session.
Basic authentication simply prompts the user for a name and password when the
administrator accesses the server. The name supplied is checked against the members of the
Administrators group on the server. Passwords are transmitted in clear text.
Windows NT Challenge Response is more sophisticated, and passwords are not transmitted
over the wire. With this security, the administrator must be logged on to his or her
computer with a username that is a member of the Administrator group on the machine they
want to administer.
When you choose between Basic and Windows NT Challenge Response, you must take into
account what is supported by the web browser you will use to administer the server. For
more information on what security is supported by different browsers, see
"Troubleshooting and Common Issues," later in this document.
In addition to these, you can also configure Web Administration to use the Secure
Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol. SSL supports authentication of users and encryption of
session data. To use SSL, in addition to setting up the server to use SSL, you must obtain
a certificate from a certificate authority such as VeriSign. For more information on SSL,
see "Securing Your Site Against Intruders," of the IIS Installation and
Administration Guide.
If your browser supports only Basic authentication, it is recommended that you also use
SSL. You may also want to use SSL even if you use Windows NT Challenge Response, because
SSL encrypts all data in the session.
If you want, you can set up a server to require the use of SSL to administer it using
the Web Administration tools. To do so, after installing Web Administration on the server,
use a web browser to connect to the server over the web to administer it. Click Maintenance,
click Web Admin Preferences, then select the Ensure use of SSL secure channel check
box and click OK. This sets the registry entry SSLRequired to 1. SSLRequired is
in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Inetsrv_NTAdmin key.
Use common sense-do not leave your workstation while logged on to an
administrative account, or during an administrative session.
If you are not familiar with Internet security, it is recommended you see the following sources to learn more about it:
For more information about general Windows NT Server security, see the
following:
Software Requirements:
You can install the software on any server that runs both of the following:
You will also need to use a Web Browser. You can run this on the server
or any computer that has network access to your server.
Before you install:
If you do not have Microsoft Internet Information Server installed on your server, please do so. Use the icon on the desktop to install Internet Information Server. You cannot install Web Administration for Microsoft Windows NT Server, unless Microsoft Internet Information Server is installed.
To install Web Administration on the server
Note: This self extracting setup program will install all the files needed into a directory on your server (%inetsrv_root%\wwwroot\NTAdmin) and make the required registry entries.
Configuring Password Authentication
Web Administration requires either "Basic" or
"NT Challenge Response" password authentication for the WWW service on the
server. IMPORTANT-- To find which type of password authentication works for the web
browser you will be using, see "Troubleshooting and Common Issues" later in this
document.
To configure password authentication
on the server
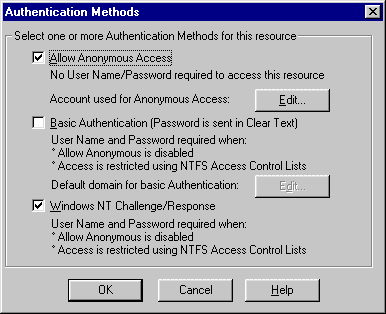
See your Microsoft Internet Information Server 4.0 documentation if you need additional information on how to configure the service.
If you have any trouble using the tools, see the next
section, "Troubleshooting and Common Issues." Be sure to check the
Browser/Password Authentication Matrix to make sure the web browser you use is compatible
with the password authentication used by the server.
Administering User Accounts
You can administer a domain's user accounts with Web Administration tools pointed at either the domain's primary domain controller or any backup domain controller.
By default, when you begin to administer user accounts using Web Administration tools, only the first 1024 user accounts are listed in the Web Administration list box, and a message appears saying that the computer is unable to list all the user accounts, and only the first 1024 are listed. This is done to save time, as it can take a while to transmit the names of all the user accounts across the network to the client browser.
Note that even with only some of the user accounts listed, you can still freely add new user accounts.
You can adjust a registry setting to have more user accounts listed when you administer user accounts. The setting is MaxUsersToDisplay, in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Inetsrv_NTAdmin key.
Problems Accessing Server
Check the Browser/Password Authentication matrix below to make sure the
browser you are using is compatible with the type of password authentication the server
uses.
Using Windows NT Challenge Response
When Windows NT Challenge Response is enabled and you are using a
browser that supports Windows NT Challenge Response, you must be logged in with an account
that has administrative privileges on the server you are administering to be able to
access and administer the server. When you use this browser and have Windows NT Challenge
Response enabled, if you are logged on with a user account that does not have privileges,
you will be prompted for a user name and password. Be sure to enter the full name (<domain_name>\<user_name>)
of a user account that is in the Administrators group on the server.
Browser/Password Authentication matrix
The following matrix shows which types of password authentication are
supported on each type of supported web browser. The "both" column is for
servers on which both Basic and Windows NT Challenge Response are enabled.
Key: "supported" means if IIS security is configured with this
authentication, you can connect with that browser.
| Basic | Windows NT Challenge | Both | |
| Internet Explorer 3.0 | Supported | Supported | Supported - rolls back to Basic. |
| Internet Explorer 4.0 | Supported | Supported | Supported - rolls back to Basic. |
| Netscape Navigator 3.0 | Supported | Not supported | Supported - rolls back to basic. |
| Netscape Navigator 4.0 | Supported | Not supported | Supported - rolls back to basic. |
Individual Tasks
This tool repeats some of the functionality found in the following
tools: Server Manager, Performance Manger, User Manager for Domains, Printer Manager, File
Manager. If you need help with one of the Administrative tasks in this tool, please see
the product documentation or the online help for these tools.
| Question | Answer |
| What browsers can an Administrator use? | The HTML pages are best viewed with Internet Explorer 4.0, but any browser that supports Basic Authentication will work. Note that not all browsers support all forms of security; see "Section 3 - What about security?" below for additional details. |
| Can a Netscape browser be used to perform the tasks? | Yes, see above. |
| What are the requirements to run this tool? | Your server must run Windows NT Server 4.0 - SP3 (or higher), Microsoft Internet Information Server 4.0 (or higher). You can then perform the task with any browser that supports Basic authentication or Windows NT Challenge Response. |
| Question | Answer |
| What tasks can be performed from the browser? | A subset of the most common tasks performed today with current administrative tools. For more information, see "Introduction to Web Administration for Microsoft Windows NT Server" earlier in this chapter. |
| Why does Internet Information Server have to be running on the server? | The tool is an ISAPI DLL and the Microsoft Internet Information Server service is required for the API calls into ISAPI.DLL. Microsoft Internet Information Server 4.0 ships with Windows NT Server 4.0 Option Pak. This can be downloaded from www.microsoft.com. |
| Can I run the Netscape Web service (instead of Microsoft Internet Information Server ) on Windows NT Server and process the ISAPI DLL calls? | No, the Netscape Web server does not support ISAPI DLLs. |
| How do the Web Administration tools scale for larger networks? | The tools are scaleable, but at a lower rate than the regular administration tools. This is because information is sent using HTTP, instead of RPC. Most tasks take a little longer with the Web Administration tools. |
| What languages are the Web Administration tools available in? | In English only. |
| Question | Answer |
| What kind of security is available? | Depends on how Microsoft Internet Information Server is configured and
what your browser supports.
|
| Can Windows NT Challenge Response be used with Netscape Browsers? | No, Netscape browsers today do not support it. |
| Can SSL encryption be used with all browsers? | Check the documentation for the browser. (Often, you can find out in the "options" menu from the browser's toolbar.) |
Web Administration of Windows NT Server is not officially supported, but some help may be provided on the web page http://www.microsoft.com/ntserver/webadmin.htm.
Web Administration of Windows NT Server is also included in the Windows NT 4.0 Server Resource Kit.
The SOFTWARE supplied in the Windows NT Server Resource Kit is not officially supported. Microsoft does not guarantee the performance of the Window NT Server Resource Kit tools, response times for answering questions, or bug fixes to the tools. However, we do provide a way for customers who purchase the Windows NT Server Resource Kit to report bugs and receive possible fixes for their issues. You can do this by either sending Internet mail to RKINPUT@MICROSOFT.COM or by referring to one of the options listed in the Start Here book, which is included with your Windows NT Server product. This mail address is only for Windows NT Server Resource Kit related issues.
The SOFTWARE (including instructions for its use and all printed and online documentation) is provided "AS IS" without warranty of any kind. Microsoft further disclaims all implied warranties, including, without limitation, any implied warranties of merchantability or of fitness for a particular purpose. The entire risk arising out of the use or performance of the SOFTWARE and documentation remains with you.
In no event shall Microsoft, its authors, or anyone else involved in the
creation, production, or delivery of the SOFTWARE be liable for any damages whatsoever
(including, without limitation, damages for loss of business profits, business
interruption, loss of business information, or other pecuniary loss) arising out of the
use of or inability to use the SOFTWARE or documentation, even if Microsoft has been
advised of the possibility of such damages.
© Copyright Microsoft Corporation, 1991-1998. All Rights
Reserved
Microsoft, Windows NT, Windows, and ActiveX are either
registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and or
other countries.
Microsoft Corporation may have patents or pending patent
applications, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights covering
subject matter in this document. The furnishing of this document does not give you any
license to these patents, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights
except as expressly provided in any written license agreement from Microsoft Corporation.
All other companies and product names are trademarks or
registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Information in this document is subject to change without
notice.